The Charpy Impact Test (or Charpy V-Notch Test) is a commonly used type of Impact Test used to determine the resistance of a material to fracture.
Charpy Impact Testing uses a pendulum testing machine which strikes the Charpy specimen and measures the energy absorbed by the specimen to determine the notch hardness of the material.
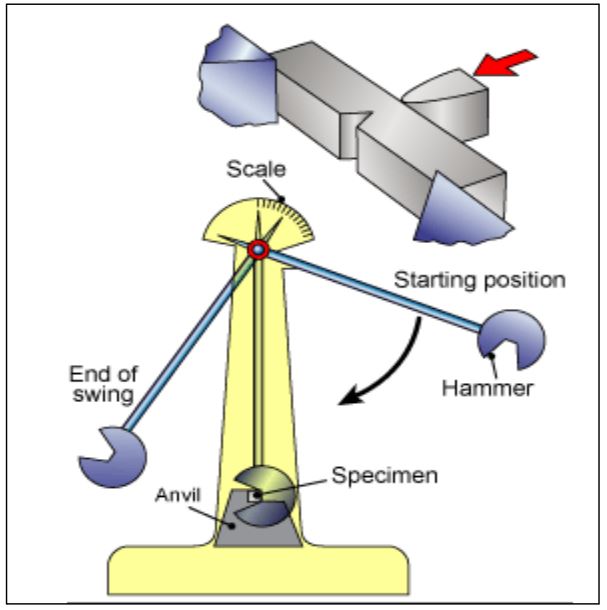
How a Charpy Impact Test Works
- The swinging pendulum weight is raised to standard height depending upon the type of specimen to be tested.
- With reference to the vise holding the specimen, the higher the pendulum, the more potential energy it has got.
- As the pendulum is released, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy until it strikes the specimen.
- The Charpy specimen is hit behind the V notch.
- A portion of the energy possessed by the pendulum is used to rupture the specimen and the pendulum rises on the other side of the machine to a height lower than its initial height on the opposite side of the impact testing machine.
- The energy consumed in breaking the specimen is the weight of the pendulum times the difference in two heights of pendulum on either side of the machine.
- This energy is the notched impact strength and can be read from the dial of the impact testing machine.
Charpy V-notch Specimen Dimensions
A Charpy-V notch specimen is measured at 55mm x10mm. The V notch is 2mm deep with a tip radius of 0.25mm.
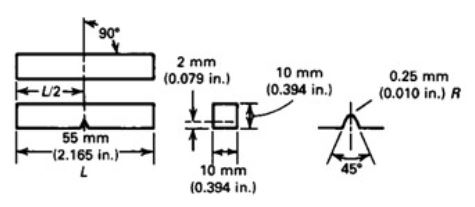
Charpy V-notch Specimen Arrangement
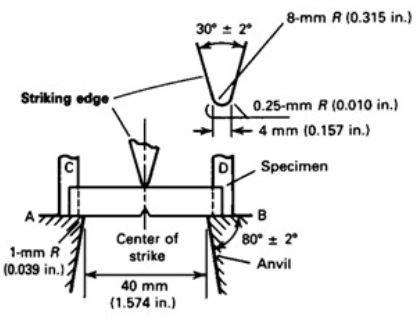
The specimen is arranged in the testing machine with the following arrangement.
Testing Temperature
Testing temperature is a key consideration and must be recorded during a Charpy Test because it greatly impacts the toughness of the material.
Multiple specimens may be tested at different temperatures to produce a graph detailing the toughness of the material in relation to temperature.
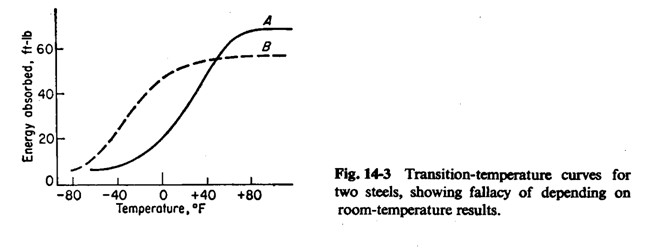
In the image above it is observed that at lower temperatures, material is more brittle. Whilst at higher temperatures, the temperature is more ductile.